“Where am I?” “Where am I going?” “How do I get there?”
Before the widespread adoption of positioning technology, clearly explaining your location and how to get to an unfamiliar place wasn't a simple task! People in the past typically used maps, celestial navigation, compasses, and other methods to solve positioning and navigation problems. Now, we can simply open our mobile phone's navigation app to obtain real-time location information and navigation services, all thanks to satellite positioning.
Satellite Positioning
The principle of satellite positioning is to determine one's position by measuring signals from beacons at known locations. Simply put, it involves measuring the line connecting a known location to the user, and the line connecting another known location to the user. The intersection of these lines is the user's location.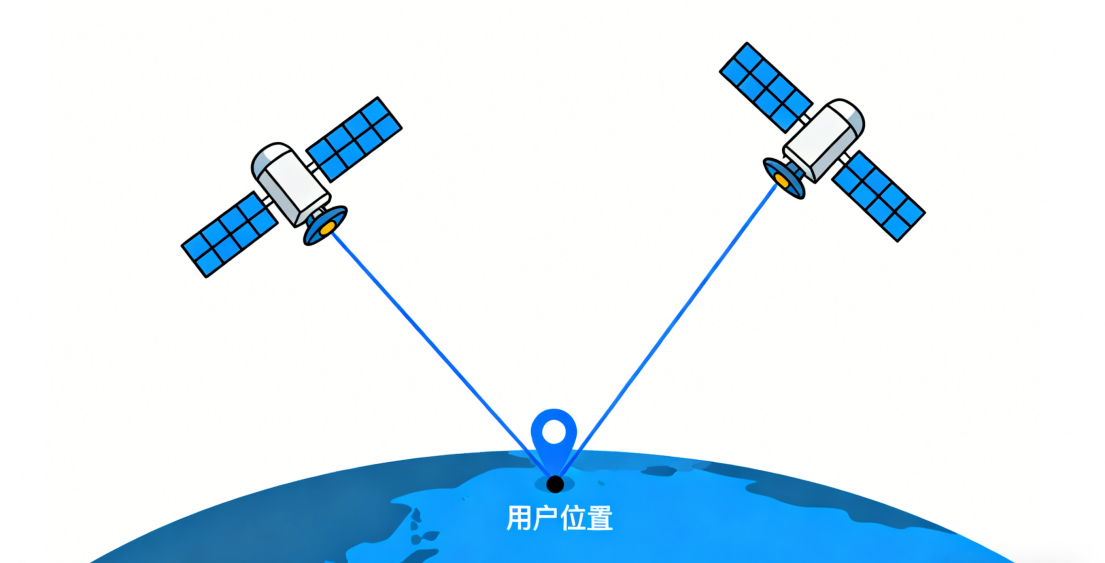
A satellite positioning module is a module used to receive signals from satellite navigation systems and calculate its own position, velocity, and time information. Smartwatches, smartphones, drones, robots, and other devices all use satellite positioning modules to achieve positioning and navigation functions.
The satellite positioning module has a built-in satellite signal receiver. By comparing the tiny differences in the arrival times of signals from different satellites, it calculates the precise distance between the positioning module and each satellite. Using the satellites as the center of spheres and the calculated distances as radii, multiple spheres are formed in space. The intersection point of these spheres is the precise three-dimensional coordinate (longitude, latitude, altitude) of the positioning module.
As can be seen, satellite positioning is a comprehensive technology based on precise timekeeping, distance measurement, and geometric positioning. Its core is accurate timekeeping; each navigation satellite is equipped with an extremely precise atomic clock and continuously broadcasts time-stamped signals to the ground.
Common Satellite Navigation Systems
· US Global Positioning System (GPS)
Developed by the US Department of Defense, it is the world's first and most widely used satellite navigation system, fully completed in 1994. GPS provides global positioning services, with civilian accuracy of about 10 meters and even higher accuracy for military use.
· Russian GLONASS System
Developed by the Soviet Union/Russia, it was first developed during the Soviet era and became fully operational in 2007. It primarily serves Russia and its surrounding areas, and has gradually expanded into a global system in recent years.
· Beidou Satellite Navigation System
This is a global satellite navigation system independently developed by China. On July 31, 2020, the China Beidou-3 global satellite navigation system was officially launched, marking the full establishment of Beidou's global service capabilities. The BeiDou Satellite Navigation System has global coverage capabilities, with civilian positioning accuracy better than 10 meters, and accuracy better than 5 meters in the Asia-Pacific region. It also supports functions such as short message communication and international search and rescue, and is widely used in surveying, transportation, logistics, and emergency rescue.
Requirements for Crystal Oscillators in Satellite Positioning Modules
As mentioned earlier, satellite positioning is a comprehensive technology based on precise time measurement for distance measurement and geometric positioning. Atomic clocks are the "time source" of the satellite positioning system, providing an absolutely precise and stable time base. Crystal oscillators are the physical tools used by the satellite positioning module receiver to measure time. Without a crystal oscillator, the receiver cannot perform the most basic time measurement, and the entire positioning process is impossible.
So, what are the main requirements of satellite positioning modules for crystal oscillators?
· High-Precision Frequency Stability
Satellite positioning relies on precise time measurement. Crystal oscillators provide a stable reference frequency for the satellite positioning module, ensuring accurate demodulation and processing of satellite signals. A stable clock signal is the foundation of the signal processing chain, and the frequency stability of the crystal oscillator directly determines the accuracy of time measurement. If the crystal oscillator performance is poor, it may lead to signal distortion or processing errors, thus affecting the accuracy of the positioning results.
· Higher Anti-Interference and Anti-Vibration Capabilities
The crystal oscillator of a satellite positioning receiver is susceptible to vibration and electromagnetic interference, leading to fluctuations in output frequency and phase. If the fluctuations are too large, it will cause the receiver loop to lose lock, resulting in the loss of satellite signals.
Crystal oscillators need to have higher resistance to electromagnetic interference and vibration. High-performance crystal oscillators, through optimized design and technologies such as metal casing shielding and ceramic packaging, can effectively resist radiation and vibration interference, ensuring stable operation in complex environments and guaranteeing the continuity and reliability of the positioning system.
· Miniaturization and Low Power Consumption
Positioning devices are trending towards miniaturization, requiring crystal oscillators to use small-sized packaging and support low-power design to extend device battery life, suitable for applications such as smart wearables and drone navigation.
· Specific Frequency Requirements
Common frequencies include 8MHz, 10MHz, 16MHz, 16.368MHz, 25MHz, 26MHz, 32MHz, etc. Different frequencies correspond to different application scenarios, and the selection should be based on the positioning module chip solution. Excellent Temperature Adaptability
On the one hand, temperature is the primary factor affecting crystal oscillator drift. The physical characteristics of quartz crystals change with temperature, leading to a drift in their oscillation frequency. On the other hand, typical operating environments for positioning devices, such as car navigation systems, outdoor mobile phones, and logistics trackers, experience a wide range of temperature variations. If the crystal oscillator cannot operate stably within this wide temperature range, positioning accuracy will decrease sharply. Generally, the operating temperature range of a crystal oscillator is typically -40℃ to +85℃ or wider, and the crystal oscillator needs to have good temperature compensation performance.
YXC provides a crystal oscillator selection guide for satellite positioning modules to help you accurately design your products.
Based on the application requirements of satellite positioning modules, YXC Yangxing Technology recommends the following crystal oscillators:
• High-precision, high-stability temperature-compensated crystal oscillator: YSO510TP series
YSO510TP Series
The YSO510TP is a high-precision, high-stability TCXO. This temperature-compensated crystal oscillator uses temperature compensation technology to achieve a frequency temperature difference as low as ±0.28 PPM (typical value ±2.5 PPM) in a wide temperature range of -30~85℃, effectively reducing positioning errors caused by crystal oscillator drift and helping to achieve high-precision positioning.
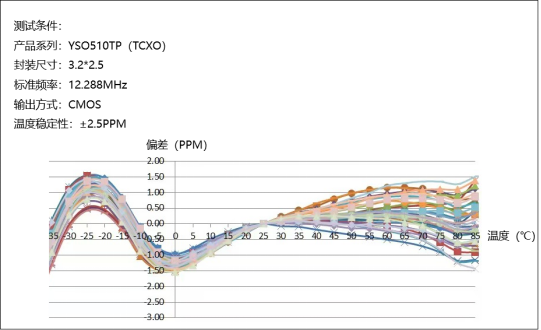
Test results: Within the operating temperature range of -30~85℃, the temperature stability of the tested samples meets ≤±2.5 PPM.
For fields with strict size requirements, such as smart wearable devices, drones, and portable positioning terminals, miniaturized positioning modules are needed. The YSO510TP can meet the miniaturization requirements of positioning modules, offering a minimum 2.0 x 1.6mm package, which helps to achieve miniaturization and compact design of the device and improve the overall integration of the device. Key Parameters:
✅ Frequency Range: 10 - 52MHz
✅ Package Size: 2.0*1.6, 2.5*2.0, 3.2*2.5, 5.0*3.2, 7.0*5.0mm
✅ Operating Voltage: 1.8/2.5/3/3.3V
✅ Output Type: CMOS, Clipped Sine Wave
✅ Operating Temperature: -30 ~ +85℃ or specify
✅ Frequency Temperature Deviation: ±0.28/0.05/0.5/1.5/2.5PPM
✅ Phase Noise: -145dBc/Hz @ 1KHz offset
· Low-Power, High-Precision, High-Stability Voltage-Controlled Temperature-Compensated Crystal Oscillator: YSV350TP Series
YSV350TP Series
Low Power Consumption Characteristics
The YSV350TP boasts excellent low power consumption characteristics, with a minimum current consumption of 6mA and a maximum of 13mA. This effectively extends the battery life of devices, and lower power consumption also reduces the requirements for battery capacity, allowing engineers to design smaller, lighter, and thinner devices. Furthermore, low power consumption means less self-heating, resulting in less frequency variation due to self-heating, and a more stable and accurate output signal.
High Precision and High Stability Characteristics
The YSV350TP series voltage-controlled temperature-compensated crystal oscillator uses a voltage-controlled temperature compensation (VC-TC) function to adjust and compensate the oscillation frequency in real time according to changes in ambient temperature, ensuring a stable and reliable clock signal under different operating conditions. The YSV350TP series achieves a frequency stability of ±0.5ppm (0℃~+50℃) and a minimum of ±1.0ppm in the operating temperature range of -40~+85℃. Key Parameters:
✅ Frequency Range: 6.4 - 60MHz
✅ Package Size: 2.0*1.6, 2.5*2.0, 3.2*2.5, 5.0*3.2, 7.0*5.0mm
✅ Operating Voltage: 1.8/2.5/3/3.3V
✅ Operating Temperature: -40~+85℃ or specify
✅ Frequency Stability: ±0.5ppm over 0℃ to 50℃ (available); ±1.0ppm over -40℃ to 85℃ (available)
✅ Phase Noise: -145dBc/Hz @ 1KHz offset